黑河生态水文遥感试验:水文气象观测网数据集(混合林站自动气象站-2014)
HiWATER: Dataset of hydrometeorological observation network (an automatic weather station of Sidaoqiao mixed forest station, 2014)
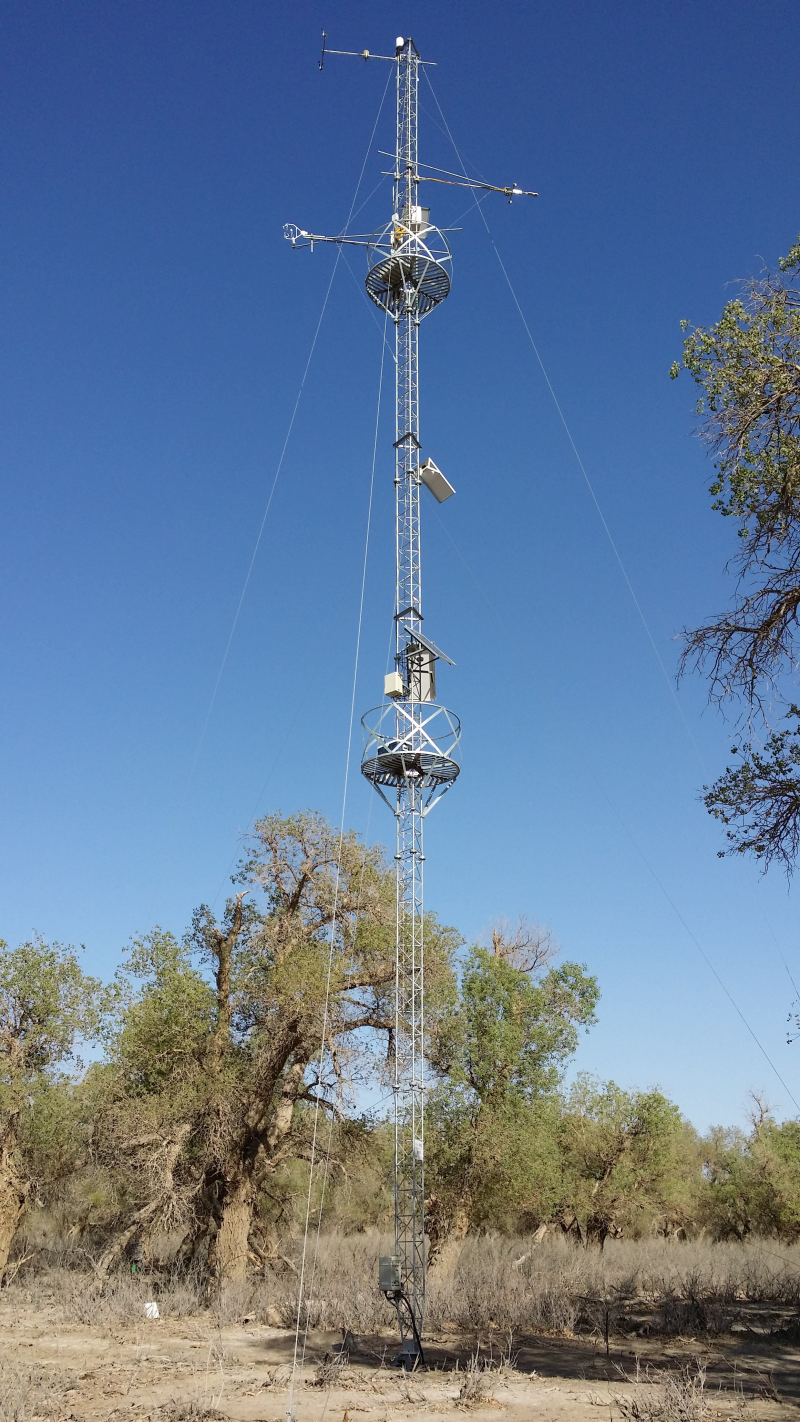

该数据集包含了2014年1月1日至2014年12月31日黑河水文气象观测网下游混合林站气象要素观测数据。站点位于内蒙古额济纳旗达来呼布镇四道桥,下垫面是柽柳与胡杨。观测点的经纬度是101.1335E,41.9903N,海拔874m。空气温度、相对湿度传感器架设在28m处,朝向正北;气压计安装在地面上的防撬箱内;翻斗式雨量计安装在28m处;风速与风向传感器架设在28m,朝向正北;四分量辐射仪安装在24m处,朝向正南;两个红外温度计安装在24m处,朝向正南,探头朝向是垂直向下;两个光合有效辐射仪安装在24m处,朝向正南,探头垂直向上和向下方向各一个;土壤温度探头埋设在地表0cm和地下2cm、4cm、10cm、20cm、40cm、60cm、100cm处,在距离气象塔2m的正南方;土壤水分探头埋设在地下2cm、4cm、10cm、20cm、40cm、60cm、100cm处,在距离气象塔2m的正南方;土壤热流板(3块)依次埋设在地下6cm处,在距离气象塔2m的正南方。
观测项目有:空气温湿度(Ta_28m、RH_28m)(单位:摄氏度、百分比)、气压(Press)(单位:百帕)、降水量(Rain)(单位:毫米)、风速(WS_28m)(单位:米/秒)、风向(WD_28m)(单位:度)、四分量辐射(DR、UR、DLR_Cor、ULR_Cor、Rn)(单位:瓦/平方米)、地表辐射温度(IRT_1、IRT_2)(单位:摄氏度)、土壤热通量(Gs_1、Gs_2、Gs_3)(单位:瓦/平方米)、土壤温度(Ts_0cm、Ts_2cm、Ts_4cm、Ts_10cm、Ts_20cm、Ts_40cm、Ts_60cm、Ts_100cm)(单位:摄氏度)、土壤水分(Ms_2cm、Ms_4cm、Ms_10cm、Ms_20cm、Ms_40cm、Ms_60cm、Ms_100cm)(单位:体积含水量,百分比)、向上与向下光合有效辐射(PAR_up、PAR_down)(单位:微摩尔/平方米秒)。
观测数据的处理与质量控制:(1)确保每天144个数据(每10min),若出现数据的缺失,则由-6999标示;由于数据采集器的原因,在2014.5.9-6.8和2014.11.9-12.7之间数据部分缺失;(2)剔除有重复记录的时刻;(3)删除了明显超出物理意义或超出仪器量程的数据;(4)数据中以红字标示的部分为有疑问的数据;(5)日期和时间的格式统一,并且日期、时间在同一列。如,时间为:2014-9-10 10:30;(6)命名规则为:AWS+站点名称。
水文气象网或站点信息请参考Li et al. (2013),观测数据处理请参考Liu et al.(2011)。
本数据要求的引用方式
文章的引用1. Liu, S., Li, X., Xu, Z., Che, T., Xiao, Q., Ma, M., Liu, Q., Jin, R., Guo, J., Wang, L., Wang, W., Qi, Y., Li, H., Xu, T., Ran, Y., Hu, X., Shi, S., Zhu, Z., Tan, J., Zhang, Y., Ren, Z. (2018). The Heihe Integrated Observatory Network: A basin‐scale land surface processes observatory in China. Vadose Zone Journal, 17,180072. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.04.0072.(查看)
2. Liu, S.M., Xu, Z.W., Wang, W.Z., Bai, J., Jia, Z., Zhu, M., & Wang, J.M. (2011). A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 15(4), 1291-1306.(查看 |下载 )
数据的引用
李新, 车涛, 徐自为, 任志国, 谭俊磊. (2016). <b>黑河生态水文遥感试验:水文气象观测网数据集(混合林站自动气象站-2014)</b>2016. doi:
10.3972/hiwater.261.2015.db.
[Li, X., Che, T., Xu, Z., Ren, Z., Tan, J. (2016). < b>HiWATER: Dataset of hydrometeorological observation network (an automatic weather station of Sidaoqiao mixed forest station, 2014)</b>2016.
doi:
10.3972/hiwater.261.2015.db. ]
(下载引用:
RIS格式 |
RIS英文格式 |
Bibtex格式 |
Bibtex英文格式
)
使用本数据时必须引用“文章的引用”中列出的文献,并进行数据的引用
参考文献
1.Zhou, J., Li, M.S., Liu, S.M., Jia, Z.Z., &Ma, Y.F. (2015). Validation and performance evaluations of methods for estimating land surface temperatures from ASTER data in the middle reach of the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sensing, 7, 7126-7156. (查看 )
2.Su, P.X., Yan, Q.D., Xie, T.T., Zhou,Z.J., & Gao, S. (2012). Associated growth of C3 and C4 desert plants helps the C3 species at the cost of the C4 species. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 34(6), 2057-2068. (查看 )
3.Song, L.S., Kustas WP, Liu, S.M., Colaizzi PD, Nieto H, Xu, Z.W., Ma, Y.F., Li, M.S., Xu, T.R., Agam, N., Tolk, J., & Evett, S. (2016). Applications of a thermal-based two-source energy balance model using Priestley-Taylor approach for surface temperature partitioning under advective conditions. Journal of Hydrology, doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.06.034. (查看 )
4.Xu, T.R., Bateni, S.M., & Liang, S.L. (2015). Estimating turbulent heat fluxes with a weak-constraint data assimilation scheme: A case study (HiWATER-MUSOEXE). IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(1), 68-72. (查看 )
5.Song, L.S., Liu, S.M., Kustas, W.P., Zhou, J., Xu, Z.W., Xia, T., & Li, M.S. (2016). Application of remote sensing-based two-source energy balance model for mapping field surface fluxes with composite and component surface temperatures. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 230-231, 8-19. (查看 |下载)
6.Zhang, L., Sun, R., Xu, Z.W., Qiao, C., &Jiang, G.Q. (2015). Diurnal and Seasonal Variations in Carbon Dioxide Exchange in Ecosystems in the Zhangye Oasis Area, Northwest China. PLOS ONE, 10(6). (查看 )
7.Bai, J., Jia, L., Liu, S., Xu, Z., Hu, G., Zhu, M., &Song, L. (2015). Characterizing the Footprint of Eddy Covariance System and Large Aperture Scintillometer Measurements to Validate Satellite-Based Surface Fluxes. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(5), 943-947. (查看 |下载)
8.Xu, Z.W., Liu, S.M., Li, X., Shi, S.J., Wang, J.M., Zhu, Z.L., Xu, T.R., Wang, W.Z., & Ma, M.G. (2013). Intercomparison of surface energy flux measurement systems used during the HiWATER-MUSOEXE. Journal of Geophysical Research, 118, 13140-13157, doi:10.1002/2013JD020260. (查看 |下载)
9.Song, L.S., Liu, S.M., William Kustas, P., Zhou, J., &Ma, Y.F. (2015). Using the Surface Temperature-Albedo Space to Separate Regional Soil and Vegetation Temperatures from ASTER Data. Remote Sensing, 7(5), 5828-5848. (查看 |下载)
10.Zhang, Q., Sun, R., Jiang, G.Q., Xu, Z.W., & Liu, S.M. (2016). Carbon and energy flux from a Phragmites australis wetland in Zhangye oasis-desert area, China. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 230-231, 45-57. (查看 )
11.Liu, S.M., Xu, Z.W., Song, L.S., Zhao, Q.Y., Ge, Y., Xu, T.R., Ma, Y.F., Zhu, Z.L., Jia, Z.Z., &Zhang, F. (2016). Upscaling evapotranspiration measurements from multi-site to the satellite pixel scale over heterogeneous land surfaces. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 230-231, 97-113. (查看 |下载)
12.Xu, Z.W., Ma, Y.F., Liu, S.M., Shi, S.J., &Wang, J.M. (2017). Assessment of the energy balance closure under advective conditions and its impact using remote sensing data. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 56, 127-140. (查看 |下载)
13.李新, 刘绍民, 马明国, 肖青, 柳钦火, 晋锐, 车涛, 王维真, 祁元, 李弘毅, 朱高峰, 郭建文, 冉有华, 闻建光, 王树果. (2012). 黑河流域生态-水文过程综合遥感观测联合试验总体设计. 地球科学进展, 27(5), 481-498. doi:10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2012.05.0481. (查看 |下载)
14.Wang, J.M., Zhuang, J.X., Wang, W.Z., Liu, S.M., &Xu, Z.W. (2015). Assessment of uncertainties in eddy covariance flux measurement based on intensive flux matrix of HiWATER-MUSOEXE. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(2), 259-263. (查看 )
15.Song, L.S., Liu, S.M., Zhang, X., Zhou, J., & Li, M.S. (2015). Estimating and Validating Soil Evaporation and Crop Transpiration During the HiWATER-MUSOEXE. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(2), 334-338. (查看 |下载)
16.Ge, Y., Liang, Y.Z., Wang, J.H., Zhao, Q.Y., &Liu, S.M. (2015). Upscaling sensible heat fluxes with area-to-area regression kriging. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(3), 656-660. (查看 )
17.Hu, M.G., Wang, J.H., Ge, Y., Liu, M.X., Liu, S.M., Xu, Z.W., &Xu, T.R. (2015). Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging. Atmosphere, 6(8), 1032-1044. (查看 |下载)
18.Gao, S.G., Zhu, Z.L., Liu, S.M., Jin, R., Yang, G.C., Tan, L. (2014). Estimating spatial distribution of soil moisture based on Bayesian maximum entropy method with auxiliary data from remote sensing. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 32, 54-66. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2014.03.003. (查看 )
19.Ma, Y.F., Liu, S.M., Zhang, F., Zhou, J., & Jia, Z.Z. (2015). Estimations of regional surface energy fluxes over heterogeneous oasis-desert surfaces in the middle reaches of the Heihe River during HiWATER-MUSOEXE. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12(3), 671-675. doi:10.1109/LGRS.2014.2356652. (查看 )
20.Xu, T., Liu, S., Xu, L., Chen ,Y., Jia, Z., Xu, Z., &Nielson, J. (2015). Temporal Upscaling and Reconstruction of Thermal Remotely Sensed Instantaneous Evapotranspiration. Remote Sensing, 7(3), 3400-3425. (查看 |下载)
21.Liu, S.M., Xu, Z.W., Zhu, Z.L., Jia, Z.Z., &Zhu, M.J. (2013). Measurements of evapotranspiration from eddy-covariance systems and large aperture scintillometers in the Hai River Basin, China. Journal of Hydrology, 487, 24-38. (查看 )
22.Li X, Cheng GD, Liu SM, Xiao Q, Ma MG, Jin R, Che T, Liu QH, Wang WZ, Qi Y, Wen JG, Li HY, Zhu GF, Guo JW, Ran YH, Wang SG, Zhu ZL, Zhou J, Hu XL, Xu ZW. Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2013, 94(8): 1145-1160, 10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00154.1. (查看 )
23.Li, Y., Sun, R., &Liu, S.M. (2015). Vegetation Physiological Parameters Setting in the Simple Biosphere Model 2 (SiB2) for alpine meadows in upper reaches of Heihe River. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(5), 755-769. (查看 |下载)
24.Wang, Binbin, Ma, Yaoming, Chen, Xuelong, Ma, Weiqiang, Su, Zhongbo, Menenti, Massimo. Observation and simulation of lake-air heat and water transfer processes in a high-altitude shallow lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015, 120(24):2015JD023863. doi:10.1002/2015JD023863 (查看 )
使用条款
本数据由“黑河生态水文遥感试验(HiWATER)”产生,用户在使用数据时请在正文中明确声明数据的来源,并在参考文献部分引用本元数据提供的引用方式。
资助项目
黑河流域生态-水文过程综合遥感观测试验:水文气象要素与多尺度蒸散发观测(91125002)
相关资源
1.黑河流域生态水文综合地图集:黑河流域沙漠(沙地)、冰川图
2.黑河生态水文遥感试验:水文气象观测网数据集(裸地站自动气象站-2013)
3.黑河生态水文遥感试验:黑河流域中游大满超级站TerraSAR-X地面同步观测数据集(2012年6月15日)
4.祁连山综合观测网:黑河流域地表过程综合观测网(混合林站涡动相关仪-2018)
6.黑河生态水文遥感试验:水文气象观测网数据集(景阳岭站自动气象站-2014)
8.黑河综合遥感联合试验:冰沟流域加密观测区K&Ka波段机载微波辐射计地面同步观测数据集(2008年3月29日)
1. 2024-11-08 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 王淑敏 用途:博士论文工作需要
2. 2024-11-08 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 王淑敏 用途:博士论文工作需要
3. 2024-11-08 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 王淑敏 用途:博士论文工作需要
4. 2022-10-25 中科院空天信息创新研究院 zhou dw 用途:研究黑河流域生态水文过程,需要该数据集,故申请下载,谢谢!
5. 2022-10-07 河海大学 杨子 用途:进行蒸散的遥感科学实验
6. 2022-09-29 西北生态环境资源研究院 冯姣姣 用途:用于黑河流域复杂下垫面的地表蒸散的估算与验证
7. 2022-08-20 中科院地理科学与资源研究所 袁梦佳 用途:用作遥感蒸散发数据的计算与验证
8. 2022-08-10 西北师范大学 薛东香 用途:论文撰写
9. 2022-07-28 北京师范大学 丁之勇 用途:博士论文 地面通量观测结合卫星遥感估算黑河流域净生态系统碳交换
10. 2022-07-23 Hohai University 刘苏仪 用途:科研
11. 2022-07-17 中国科学院空天信息创新研究院 张逸卿 用途:博士论文,基于机器学习的蒸散发估算研究,导师贾立
12. 2022-07-16 北京师范大学 刘强 用途:科研用途,用于真实性检验与尺度转换研究,研究区域包含本站点
13. 2022-07-14 Hohai University 刘苏仪 用途:科研
14. 2022-07-14 Hohai University 刘苏仪 用途:科研
15. 2022-05-23 江苏海洋大学 陈晨 用途:学习研究
16. 2022-05-23 江苏省苏州市张家港市乐余镇有机玻璃厂 陈佳婷 用途:学习研究
17. 2022-05-23 江苏省苏州市张家港市乐余镇有机玻璃厂 陈佳婷 用途:学习研究
18. 2022-05-16 广州地理研究所 许剑辉 用途:对黑河流域地表温度进行研究
19. 2022-05-12 电子科技大学 唐文彬 用途:遥感地表温度验证、站点数据收集 导师:周纪教授 基金:自然基金面上项目,多源遥感协同下的全天候地表温度反演方法(41871241)
20. 2022-05-07 西南大学 陶思诺 用途:论文结果验证
暂无数据
数据评论
登录 后可以添加数据评论。

 Copyright ©right; 2017 - 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 - 兰州数云软件科技有限公司提供技术支持
Copyright ©right; 2017 - 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 - 兰州数云软件科技有限公司提供技术支持