HiWATER: Net Primary Productivity product of the Heihe River Basin
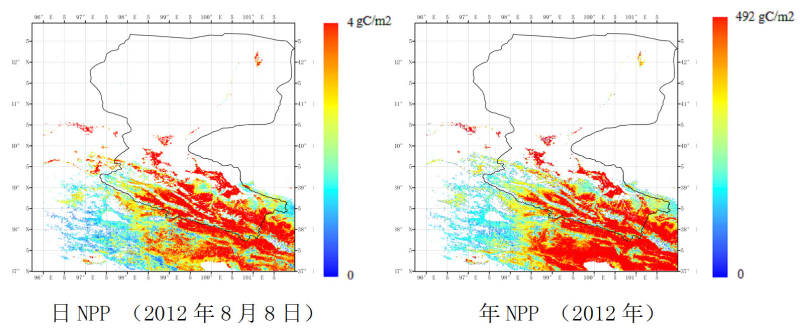
Biological productivity refers to the material production capacity of organisms and their groups or even larger scale (including ecosystem and biosphere). It changes with the environment. Therefore, it becomes an indicator of environmental change and the health of the earth system. Net primary productivity (NPP) of vegetation refers to the remaining part of total organic matter (GPP) produced by photosynthesis of green plants in unit time unit area after deducting autotrophic respiration (RA). The NPP products in Heihe River Basin mainly focus on the important parameters par and FPAR of the model of light energy utilization, and improve the algorithm and product production. The FPAR inversion model that distinguishes the direct radiation from the scattered radiation and the par inversion method based on the combination of static and polar orbit satellites are proposed. Finally, the net primary productivity data set of Heihe River Basin is produced by using the light utilization model. The algorithm improves the temporal and spatial resolution of data products, and the accuracy of products is also significantly improved.
Data Citations
Related Literatures:1. Li, X., Liu, S.M., Xiao, Q., Ma, M.G., Jin, R., Che, T., Wang, W.Z., Hu, X.L., Xu, Z.W., Wen, J.G., Wang, L.X. (2017). A multiscale dataset for understanding complex eco-hydrological processes in a heterogeneous oasis system. Scientific Data, 4, 170083. doi:10.1038/sdata.2017.83.(View Details |Download )
Cite as:Li, L., Zhong, B., Wu, J., Wu, S., Xin, X. (2017). < b>HiWATER: Net Primary Productivity product of the Heihe River Basin</b>2017. doi: 10.3972/hiwater.290.2016.db. (Download the reference: RIS | Bibtex )
Using this data, the data citation is required to be referenced and the related literatures are suggested to be cited.
References literature
1.Li Xin, Liu Shaomin, Ma Mingguo, Xiao Qing, Liu Qinhuo, Jin Rui, Che Tao. HiWATER: An Integrated Remote Sensing Experiment on Hydrological and Ecological Processes in the Heihe River Basin. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(5): 481-498. (View Details |Download)
2.Li X, Cheng GD, Liu SM, Xiao Q, Ma MG, Jin R, Che T, Liu QH, Wang WZ, Qi Y, Wen JG, Li HY, Zhu GF, Guo JW, Ran YH, Wang SG, Zhu ZL, Zhou J, Hu XL, Xu ZW. Heihe Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2013, 94(8): 1145-1160, 10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00154.1. (View Details )
Terms of Use
To respect the intellectual property rights, protect the rights of data authors, expand services of the data center, and evaluate the application potential of data, data users should clearly indicate the source of the data and the author of the data in the research results generated by using the data (including published papers, articles, data products, and unpublished research reports, data products and other results). For re-posting (second or multiple releases) data, the author must also indicate the source of the original data.
Support Program
The CAS (Chinese Academy of Sciences) Action Plan for West Development Project
National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program)
Related Resources
2.Physical and chemical index data of deep drilling strata in the middle reaches of Heihe River (2013)
3.HiWATER: the albedo in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin (Jun. 29, 2012)
5.HiWATER: Airborne CCD image data in Hulugou Catchment
7.A survey construction of a water-saving society in Zhangye city, Gansu (2013)
10.HiWATER: Airborne CCD image data in the Shenshawo desert area of the Heihe River Basin
No record
No record
Comments
Sign In to add comments
Keywords
Geographic coverage
| Spatial coverage |
East:101.98 South:37.02 |
West:95.99 North:43.01 |
|---|
Details
- Format: ENVI标准格式
- File size: 4.16 MB
- Browse count:10042
- Temporal coverage:2013-01-17 To 2015-01-16
- Access: Offline
- Updated time:2021-04-19
Authors
Resource Provider: LI Li ZHONG Bo WU Junjun WU Shanlong XIN Xiaozhou

 Copyright ©right; 2017 - 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 - 兰州数云软件科技有限公司提供技术支持
Copyright ©right; 2017 - 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院 - 兰州数云软件科技有限公司提供技术支持